symlinker: Create Symlink, Hardlink, And Directory Junction In Windows
If you rely on mklink Windows command line utility to create symbolic links for files and folders but hate using frustratingly tiring /D, /H, and /J switches to create symlinks, hardlinks, and folder junctions, respectively, we have a neat, little utility for you – symlinker (a.k.a Symbolic Link Creator) is GUI alternative to mklink utility that lets you create file and folder symbolic links for all three widely used link types, Symbolic link, Hardlink, and Directory junction. For those who haven’t heard about such files and folder links before, read on for a brief intro on each type of link.
Symbolic file link, casually known as symlink, is just like a Windows shortcut with one major difference; it registers itself on the file system, and hence takes no disk space, whereas shortcut usually takes 1KB on disk. When the symlink is deleted, only the pointer used by file system to redirect the request by user to target location gets removed. You can create file symlink using mklink command (without switch) and folder symlink with /D switch in CMD tool.
The hardlink, in theory, works only for files and is responsible for cloning the linked data for retaining the original file even if it’s deleted. Using the /H mklink command switch, you can create hardlinks for files in Windows. The changes made to original file will be reflected in linked file. However, on deleting the original file, the linked file will not be removed.
When you want hardlink for folders, /J should be used; it creates folder junctions which works just like a file hardlink. The directory junction seems quite akin to folder shortcut, but in real, it’s quite different. The advantage of directory junction over Windows shell shortcut (which acts as a pointer for target folder) is that Directory Junction enables you to access files from within the folder and can be accessed from both Windows Explorer and Command Prompt.
To create a symbolic link for folder or file, pick the symlink type. Depending upon the type, enter the source and target locations. For instance, if you want to create file symlink, enter the complete path of folder where you want to save the link followed by link name. Now specify the file which is to be linked. Once done, select the type of link; Symbolic Link or Hard Link.
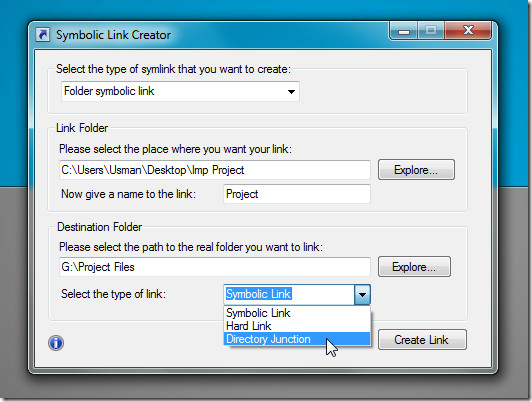
Clicking Create Link will create a link at defined target location. Similarly, you can create other types of file and folder symbolic links at required locations.
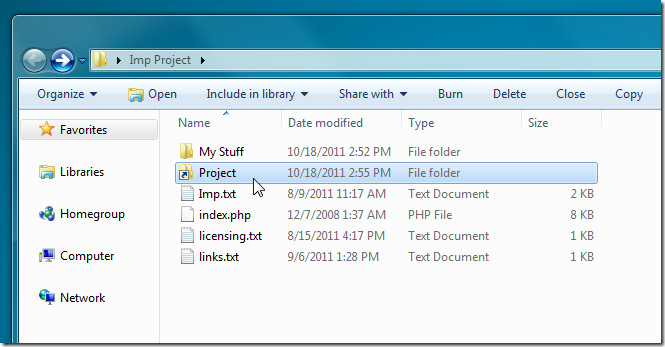
symlinker doesn’t show errors and warnings when you attempt to create hardlinks for folder or specify an incompatible path in Destination Folder input field. It’s an open source application that works on Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7.

Worked really well for me on Win8. Thank you!!!
This is a simple GUI just for mklink call in Windows Vista/7. It uses .NET Framework for doing such simple job!!!! And It does not work in Windows XP!!!!!!!!!! Correct post in this blog!
Windows XP doesn’t have the mklink command available from the cmd.exe app.
You might want to check out Link Shell Extension (http://schinagl.priv.at/nt/hardlinkshellext/hardlinkshellext.html) which does the same thing from the right click & drag in Windows Explorer. It makes it so much easier to drag from one folder to another rather than using a separate program to specify the file locations.