How To Disable/Turn off System Restore In Windows 7 / Vista / XP
Whenever users install software program, drivers, updates, hotfixes and other system changing files, Windows Vista and Windows Xp creates a Restore Point by using System Restore, where a snapshot and stored state of important system files are backed up and copied, If anything goes wrong such as driver not working or program causes instability to the system, users can easily rollback to the previous state. If you pretty sure that you practice safe computing and can handle all disaster yourself, you can turn off and disable System Restore in Windows Vista and Windows Xp. Learn how to do it, after this jump.
Disable System Restore In Windows Xp
Right Click My Computer on your desktop, or click Start and it will be listed in the menu.
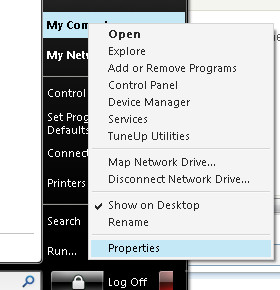
Click Properties, and above the General tab click the System Restore tab.
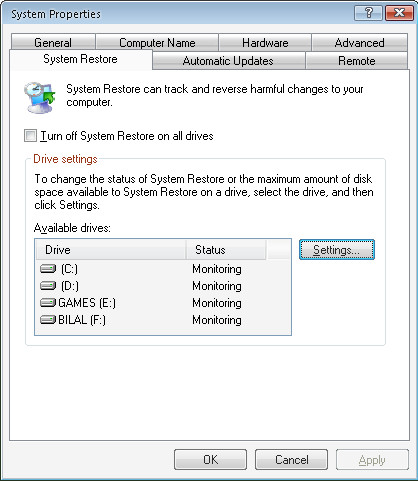
Click the check box Turn Off System Restore on all drives.
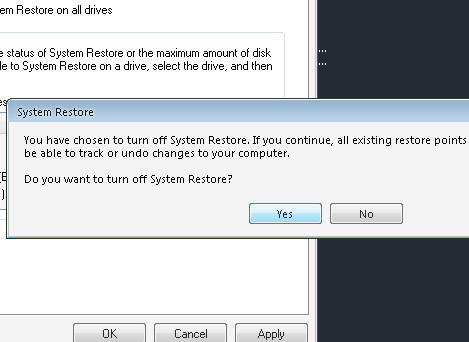
Disable System Restore In Windows Vista or 7
Right click on Computer, select Properties from contextual menu or click on Control Panel > System and Maintenance > System.
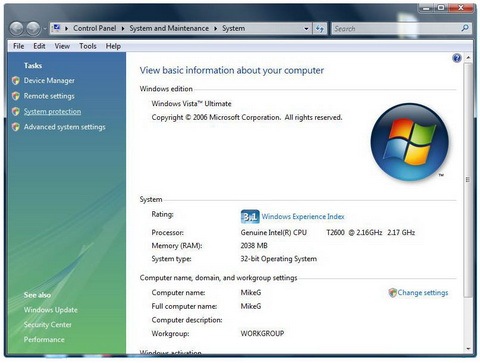
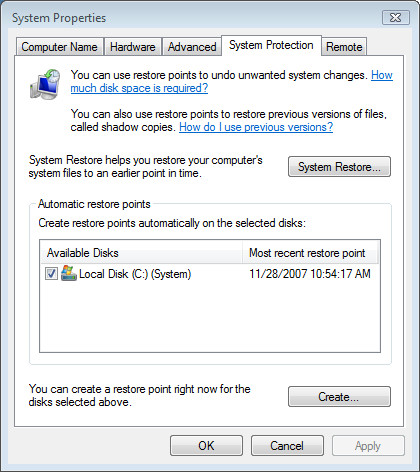
In the left pane, click System Protection. If you are prompted for an administrator password, type the password or provide confirmation. You will see a list of hard disk drives, the check boxes with ticks indicate that System Restore is on for that particular volume. So to to turn off System Protection, clear the check box next to the disk.
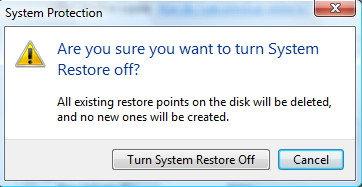
Now a System Protection dialog box will appear. Click on Turn System Restore Off button. Click OK and System Restore is now off.
To revert and enable or turn on System Protection for a hard disk, simply select (tick) the check box next to the disk, and then click OK.

Disable the paging file? Not a good idea unless you have a ridiculous amount of memory. it’s there for a reason, to ensure you don’t run out of memory and that memory gets used efficiently.