Convert Your Computer Into Live Video Streaming Server
Services like UStream and JustinTv are a good platforms to broadcast live videos, but what if you want to convert your computer into a video streaming server? BroadCam is a free tool for Windows that let’s you stream live videos over both local network and internet. Apart from basic live streaming, you can also stream pre-recorded videos instantly. The pre-recorded videos can be either in Divx(AVI format), Windows ASF AND WMV files, or DV videos files.
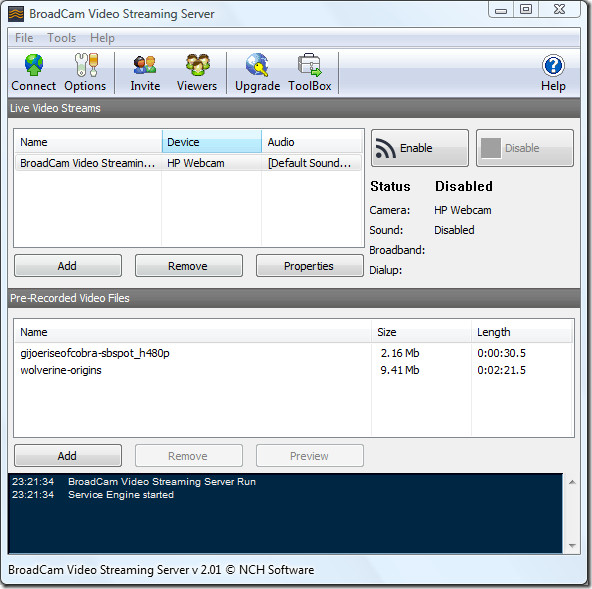
On the main window, you will find options to add both live video streams and pre-recorded video files. Once you are ready to stream the video, click Connect. You can change the status of your Webcam by hitting Enable/Disable button.
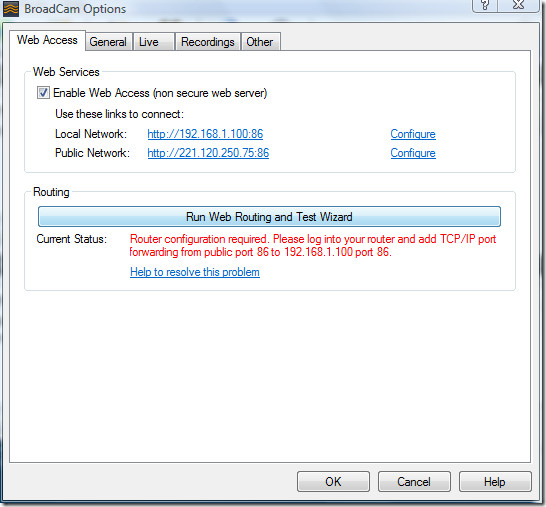
Go to Options and it will provide you with the network address that you can share with your friends, both local network and public network are given. If you are using a router then you will have to forward it, the details of which are given next to Current Status.
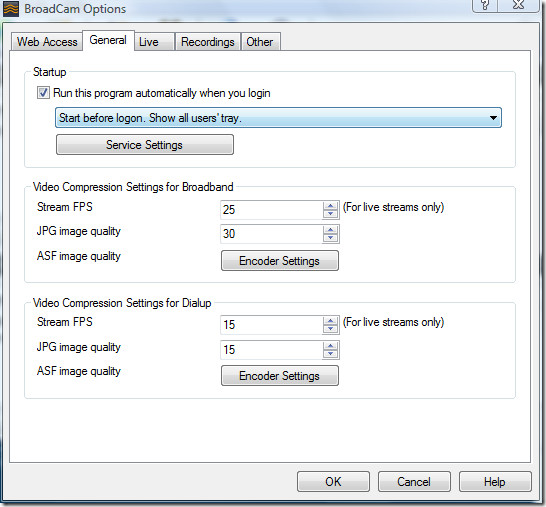
There are loads of other options such as you can change the way program starts, and also change the video compression settings for both Broadband and Dial-Up streams.
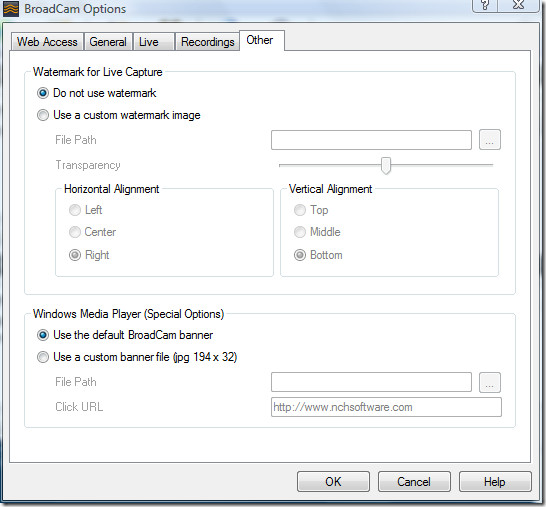
You can also set the options for broadband or dialup quality streams of both Live and Pre-recorded videos. Your viewers can select between the broadband and dial-up quality streams depending on their internet connectivity. If a lot of people are watching your video, you can add a custom watermark or a clickable banner image.
Overall, it’s a great tool that generates a custom page where people can come and watch your live streaming videos. What’s great is that it does not require some technical knowledge to setup, all you have to do is set up your webcam or select the videos and hit Connect. It does not disturb your other computer activities, since it sits silently in the system tray. It works on Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7. It supports both 32-bit and 64-bit OS. Enjoy!

I’ve had success using Flash Media Encoder to stream from a webcam to nex gen media server running on my local box. The NGMS media server can then take the webcam feed and convert it to send over the internet to an iphone or another pc. These are the directions I used http://forum.ngenbits.com/index.php?topic=48.0
broadcam isn’t free at all. the free version operates for maybe a half hour at most then it asks you to buy the pro version after kicking you off their server.
I am currently using broadcam but some time it is too slow.Thanks for sharinghttp://freecomputercourses.blogspot.com
Web casting, or broadcasting over the internet, is a media file (audio-video mostly) distributed over the internet using streaming media technology. Streaming implies media played as a continuous stream and received real time by the browser (end user). Streaming technology enables a single content source to be distributed to many simultaneous viewers. Streaming video bandwidth is typically calculated in gigabytes of data transferred. It is important to estimate how many viewers you can reach, for example in a live webcast, given your bandwidth constraints or conversely, if you are expecting a certain audience size, what bandwidth resources you need to deploy.To estimate how many viewers you can reach during a webcast, consider some parlance:One viewer: 1 click of a video player button at one location logged onOne viewer hour: 1 viewer connected for 1 hour100 viewer hours: 100 viewers connected for 1 hour…Typically webcasts will be offered at different bit rates or quality levels corresponding to different user’s internet connection speeds. Bit rate implies the rate at which bits (basic data units) are transferred. It denotes how much data is transmitted in a given amount of time. (bps / Kbps / Mbps…). Quality improves as more bits are used for each second of the playback. Video of 3000 Kbps will look better than one of say 1000Kbps. This is just like quality of a image is represented in resolution, for video (or audio) it is measured by the bit rate.
Web casting, or broadcasting over the internet, is a media file (audio-video mostly) distributed over the internet using streaming media technology. Streaming implies media played as a continuous stream and received real time by the browser (end user). Streaming technology enables a single content source to be distributed to many simultaneous viewers. Streaming video bandwidth is typically calculated in gigabytes of data transferred. It is important to estimate how many viewers you can reach, for example in a live webcast, given your bandwidth constraints or conversely, if you are expecting a certain audience size, what bandwidth resources you need to deploy.To estimate how many viewers you can reach during a webcast, consider some parlance:One viewer: 1 click of a video player button at one location logged onOne viewer hour: 1 viewer connected for 1 hour100 viewer hours: 100 viewers connected for 1 hour…Typically webcasts will be offered at different bit rates or quality levels corresponding to different user’s internet connection speeds. Bit rate implies the rate at which bits (basic data units) are transferred. It denotes how much data is transmitted in a given amount of time. (bps / Kbps / Mbps…). Quality improves as more bits are used for each second of the playback. Video of 3000 Kbps will look better than one of say 1000Kbps. This is just like quality of a image is represented in resolution, for video (or audio) it is measured by the bit rate.
Web casting, or broadcasting over the internet, is a media file (audio-video mostly) distributed over the internet using streaming media technology. Streaming implies media played as a continuous stream and received real time by the browser (end user). Streaming technology enables a single content source to be distributed to many simultaneous viewers. Streaming video bandwidth is typically calculated in gigabytes of data transferred. It is important to estimate how many viewers you can reach, for example in a live webcast, given your bandwidth constraints or conversely, if you are expecting a certain audience size, what bandwidth resources you need to deploy.To estimate how many viewers you can reach during a webcast, consider some parlance:One viewer: 1 click of a video player button at one location logged onOne viewer hour: 1 viewer connected for 1 hour100 viewer hours: 100 viewers connected for 1 hour…Typically webcasts will be offered at different bit rates or quality levels corresponding to different user’s internet connection speeds. Bit rate implies the rate at which bits (basic data units) are transferred. It denotes how much data is transmitted in a given amount of time. (bps / Kbps / Mbps…). Quality improves as more bits are used for each second of the playback. Video of 3000 Kbps will look better than one of say 1000Kbps. This is just like quality of a image is represented in resolution, for video (or audio) it is measured by the bit rate.