Understand Root Certificates and Their Importance
If you’ve never had root certificates explained to you before, the topic can seem daunting at face value. In today’s guide, we’ll cover all the key points of the encryption process you need to know in order to make safer decisions online. Additionally, we’ll cover the best VPNs to help enhance your Internet security.
Encryption has a simple role in the digital world: wrap data in a cloak of security so only the intended recipient can read it. The process is a lot like creating a key and a lockbox for every piece of information that leaves your computer. The cryptography behind the process is incredibly complex, as is the process used to initiate the exchange and verify keys. After all, creating an unbreakable lock doesn’t do you much good if anyone can get ahold of the key.

This is where certificates come into play. These tiny files are a fundamental part of public key cryptography used by browsers and HTTPS sites to validate certain types of encryption. In other words, certificates ensure everyone is who they claim to be, preventing malicious hackers and invasive third parties from stepping in and spying on your activity.
Take your cybersecurity into your own hands with these powerful VPNs:
- NordVPN – Most Secure VPN – NordVPN is the “kitchen sink” provider, with ever relevant privacy provisions under the sun. Guarantee ready access to the free and open Internet with the world’s most trusted VPN.
- Surfshark – An affordable VPN that doesn’t skimp on encryption or performance.
- ExpressVPN – Super-fast provider ideal for unblocking Netflix streams without buffering.
- IPVanish – The torrenter’s delight; allows for fast, secure downloads anywhere in the world.
Root certificates sit at the heart of the entire certificate system to make sure they operate as intended. It’s an intricate world with a lot of jargon to wade through, but knowing how certificates work can give you a much better understanding of how the internet operates on a day to day basis. Keep reading for a guide on root certificates and their role in online privacy and security.
Public and Private Key Cryptography
Before we can jump into root certificates, there are a few general cryptography terms you should get familiar with. Symmetric and asymmetric encryption are two methods of securing data that involve generating keys that unlock a very specific encryption code. Each method does things slightly different. For our purposes, public key encryption is the most important.
Public Key Encryption (asymmetric) – Two mathematically matching keys are generated: a public key and a private key. Anything encrypted using one key can only be decrypted by the other. The same key can’t even decrypt the data it previously encrypted.
Private Key Encryption (symmetric) – Two identical private keys are generated the moment data is encrypted. Anyone with either of these keys can encrypt and decrypt data secured by the other key.
Asymmetric encryption is incredibly useful for verifying the origin of encrypted data. If you have a public key and your friend has the matching private key, you can use them to securely exchange messages. Write a note and encrypt it using your key, safe in the knowledge that no one can read it, not even yourself! When your friend receives the message, he’ll know it came from you because his key could decrypt it. It’s a simple form of identity verification, but it creates the foundation of an incredibly useful security system that powers the digital world.
Encryption and HTTPS
With the two types of encryption out of the way, let’s move to the web’s version of private communication, HTTPS. The “S” added to the end of HTTP stands for “secure”, you probably recognize it from the little lock icon that often appears in your browser’s URL box. In practice HTTPS is simply standard HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) with a little SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption added on top. It basically ensures standard internet traffic can’t be read by third parties, and it uses encryption and certificates to accomplish this.
When you visit a website that uses HTTPS, a conversation takes place between your browser and the site you’re attempting to access. Your browser starts the process and requests some secure data. The site responds and sends over its public key. Your browser uses the public key to encrypt data that only the website can decrypt (using its matching private key). When the site sends something back, your browser uses the public key to decrypt the data encrypted by the server’s private key, and so on.
The only problem with this portion of the process is that there’s no way to tell if the owners of the keys are who they claim to be. Anyone could theoretically take control of a public or private key and masquerade as your favorite HTTPS site, which isn’t secure at all. This is where certificates and Certificate Authorities come into play.
RELATED READING: What is DNS Hijacking, Explained: How to Stop DNS Hijacking?
About Certificates and Certificate Authorities
Certificates are a bit like passports or a driver’s license for encrypted data. Each one is issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), which allows them to be verified and given out to only legitimate parties. The process of getting and utilizing a certificate for an HTTPS website looks something like this:
- To secure a site with HTTPS, an admin must request a certificate from a Certificate Authority.
- After verifying the authenticity of the admin, the CA generates a public and private key for the site to use.
- The public key is signed by the CA, which encrypts it with their own private key.
- The site owner receives an encrypted and unencrypted version of the public key.
- The website is secured with HTTPS and will send the public key to browsers that make data requests.
With certificates in play, the process of connecting to an HTTPS site now has an extra step. Your browser requests data from an HTTPS site. The site responds and sends over its public key. Your browser decrypts the key and checks the signature to make sure it was generated by the Certificate Authority and is valid. If it is, the transaction continues as normal, with all data being encrypted both ways.
Root Certificates
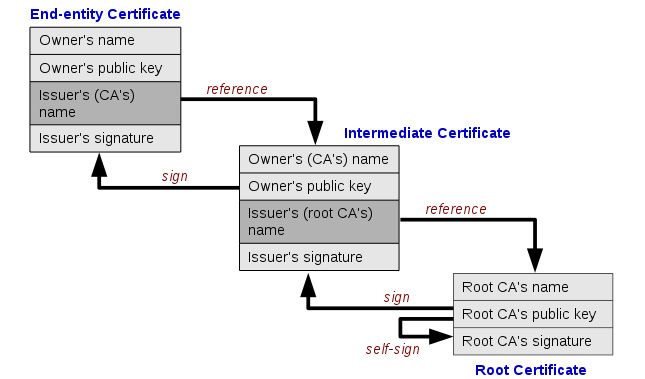
Certificates are granted to HTTPS websites through Certificate Authorities in a sort of tree like structure. Each verification extends out to create new certificates but also references the certificate that came before it. All of these can be traced back to a core certificate that originated the signing process. This is known as a root certificate, and they form the root that ensures the entire validation chain can be trusted.
An example is probably in order. Let’s say you want to start your own website that uses HTTPS. You contact a Certificate Authority and request a certificate. They verify you are who you claim to be, collect a small payment, and issue your keys. This CA isn’t a root certificate authority, however. The certificate you were given was issued by another CA. That CA’s certificate was in turn issued by another CA, and so on. Eventually the issuing party can be traced back to a root certificate, making the rest intermediate certificates that form a verification chain.
There are hundreds of Certificate Authorities in operation around the world who distribute certificates to a variety of businesses. Root certificates are incredibly important, though, which is why they’re usually only released by operating system developers like Microsoft and Apple and a few browser developers such as Mozilla and Opera.
What Does a Certificate Look Like?
Certificates are files just like any other. They’re incredibly small, no more than a few KB in size, which makes them easy and fast to transfer between servers and any kind of connected device. You’ll actually find a few on your local operating system by searching for the .crt extension. Just make sure not to delete or alter any of these, as that can cause some serious problems.
Opening a certificate in a text editor shows a block of randomized numbers and letters generated by a complex cryptography algorithm. This is the cipher key which unlocks matching encryption created using the paired private key. The file doesn’t make a lot of sense to human eyes, but when a certificate goes to work, it accomplishes a lot.
RELATED: Vishing Explained: What Is Voice Call Phishing and How to Protect Yourself
Fake Certificates and False CAs
The purpose of the certificates system is to add a layer of trust to the key swapping process. If a website or a software developer’s identity can be proven, the transaction is safe to carry out. Problems do arise in the verification system, however. Fake certificates have been known to exist, and at least one CA has been discovered issuing fake certificates. Most of these are generated from government level maneuvers carried out in secret, though individual hackers are also capable of compromising the system.
From an end user’s perspective, there’s very little we can do to prevent fake certificates from causing harm. The best protection is to watch the websites we’re using and avoid them if they seem a little suspicious. It’s entirely up to the certificate authorities to detect and remove false sources when and if they arise. There are ways to remove root certificates from your own operating system, but it’s generally considered a fruitless action that causes more harm than good.
Staying Safe with a VPN
Although the burden of security with certificates is largely up to CAs, users do have a few tools that can help stabilize other parts of the internet. Virtual private networks are one of the more commonly used methods of encrypting and anonymizing online traffic. With a VPN you’ll fend off a variety of man-in-the-middle attacks that target local internet service providers as well as users whose data isn’t encrypted. It’s a base level form of privacy, but it’s remarkably effective.
VPNs are easy to use and offer a wide variety of features that extend well beyond online anonymity and security. For starters, you’ll be able to change your virtual location to access geo-restricted videos from other countries, protect your mobile devices from harmful public Wi-Fi connections, bypass censorship blocks, defeat ISP throttling, and even hide your traffic from ISPs and mass surveillance efforts. All you have to do is choose a reliable VPN, run the software, and you’re good to go.
Below are a few recommended VPN services that place a high priority on privacy and security. Try any one of them and you’ll see just how straightforward and powerful a good VPN can be.
1. NordVPN

NordVPN is a well-known and highly respected VPN. The company has an absolutely massive network of servers, over 5,200 in 60 different countries, which could be the largest in the entire VPN marketplace. This gives you an impressive variety of options when you need to select an out of country connection for video streaming or bypassing censorship blocks. NordVPN’s entire server network is also incredibly fast, and you gain access to that speed without sacrificing an ounce of privacy or security.
A few of NordVPN’s best features:
- Strong privacy features allow open access to the internet even in censorship-heavy countries like China.
- Zero-logging policy that covers everything from traffic to bandwidth, IP addresses, and timestamps.
- Unique double encryption servers that wrap data in 2048-bit SSL encryption.
- An excellent VPN with reliable and fast access to Netflix.
Read our full NordVPN review.
- Unblocks American Netflix
- No bandwidth caps
- No IP/DNS leaks found
- Extra-secure Double VPN for data encryption
- 30-day money back guarantee.
- Very little
- Refund processing can take up to 30 days.
2. Surfshark

Surfshark offers only the most modern privacy provisions in an affordable package. Unblock sites and dodge surveillance via OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPSec, WireGuard connections, secured by unbreakable 256-AES-GCM encryption. There are over 800 servers total in 50 countries, with options for static IP addresses and even multi-hop routing. CleanWeb anti-malware protects you from poor browsing habits, while a solid logging policy guarantees your anonymity.
Surfshark comes complete with these advanced features:
- RAM-only server network incapable of storing logs of your activity.
- Unlimited simultaneous connections to protect all your devices.
- Zero caps on bandwidth, restrictions on traffic type, or server switching.
- NoBorders anti-censorship method that can break China’s Great Firewall.
- Bypass government censorship with NoBorders mode
- Get a static IP from US, UK, Germany, Japan, or Singapore
- IP, DNS and WebRTC leak protection plus kill switch
- Logging policy independently audited and verified
- Refund requests are simple and fast–no waiting or hassle.
- Growing network doesn’t have same coverage as more mature VPNs
- New-kid-on-the-block status may not instill same trust as larger providers.
Read our full Surfshark review.
3. ExpressVPN

ExpressVPN is all about speed. The company runs a large network of over 3,000 servers in 94 different countries, providing users with convenient access to lag-free connections no matter where they’re located. Each of these servers delivers incredible speeds all throughout the day, even during times of peak use or high user load. Best of all, you can check a server’s latency and speed score from within ExpressVPN’s software and change locations instantly, ensuring you always find the fastest connection possible.
Other features that we love about ExpressVPN:
- Easy to use custom apps for Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, and more.
- Reliable access Netflix, even when other VPNs are blocked.
- Unlimited bandwidth, no speed caps, and no throttling.
- DNS leak protection and an automatic kill switch.
- Great for bypassing censorship in countries like China.
Read our full ExpressVPN review.
- Unblocks US Netflix, BBC iPlayer, Hulu and Amazon Prime
- Fast serves with minimal speed loss
- Govt-level AES-256 encryption
- Keeps no logs of personal data
- Live Chat Support.
- Slightly pricier than competition.
4. IPVanish
IPVanish is a great VPN for anyone who wants to remain invisible online. It starts with strong 256-bit AES encryption for all of your data, wrapping everything in an unbreakable shell that keeps it hidden as it travels through your ISP. That encryption is backed up with an incredible zero-logging policy on all traffic that passes through IPVanish’s servers. The network itself is over 850 nodes strong, covering 60 different countries with over 40,000 IP addresses to use. Every time you connect to IPVanish you leave your personal identity behind, making the entire internet as open and safe as possible.
IPVanish also comes with the following features:
- Fast and easy to use software for PC, laptops, smartphones, Chromebooks, and tablets.
- Unlimited bandwidth, no speed caps, and no restrictions on P2P or torrent traffic.
- Secure, fast, and anonymous downloads ideal for torrent and Kodi users.
- Perfect for bypassing censorship filters and accessing blocked content.
Read our full IPVanish review.
If you need a VPN for a short while when traveling for example, you can get our top ranked VPN free of charge. NordVPN includes a 30-day money-back guarantee. You will need to pay for the subscription, that’s a fact, but it allows full access for 30 days and then you cancel for a full refund. Their no-questions-asked cancellation policy lives up to its name.
