Protecting Online Freedom with Alternative Encryption
For many people, encryption is just a software feature that you turn “on” to make the Internet safe. But, VPNs with alternative encryption methods enable you to do so much more. In an age where net neutrality is no longer guaranteed, use our recommended VPNs to restore and maintain access to the free and open Internet.

With net neutrality officially repealed in the United States, the future of a free and open internet hangs on the balance. While there are still windows for the motion to be overturned, no one’s waiting around for the worst to happen.
Savvy internet users are loading up with knowledge about encryption methods and other ways to preserve their own online freedoms. VPNs are a great place to start, but they’ll likely be the first thing ISPs start blocking. Good thing there are several other popular, workable, and almost unblockable alternative encryption methods you can use to save net neutrality on your own devices.
Take control of your right to privacy online with these resilient, powerful VPNs:
- NordVPN – Best for Net Neutrality – Don’t let ISPs determine your online privileges, tunnel through to the free and open Internet with the world’s most powerful VPN. Make use of Onion over VPN, obfsproxy, SSL tunnels, and the cutting-edge NordLynx protocol.
- Surfshark – The best VPN to come out post Net Neutrality, with powerful tunneling protocols and auto-obfuscation to dodge VPN-blockers.
- ExpressVPN – A reliable workhorse of the VPN industry, with blazing-fast connections made even more secure with the launch of Lightway encryption.
Encryption – How it Works, Why it Works
Encryption is simple in concept but complex in execution. Fortunately you don’t need a double PhD in higher mathematics and computer science to put it to use. At its core, encryption is all about complex cryptography patterns forming mathematical puzzles that are practically unsolvable without the right set of keys. No human could ever break encrypted data, and it would take an advanced computer millions of years to crack it by force. For this reason, encryption is perfect for keeping information hidden from outside eyes. It’s that safety that makes it perfect for saving net neutrality, as well.
The Encryption Process
Encryption is a lot like sending a postcard through the mail. It starts at your home, on your PC, smartphone, or other internet connected device. You want to send a packet of data out to the world wide web. Let’s say it’s a simple request to load a website or fetch your e-mail. The normal method is to send the packet through your router stamped with your devices local IP address, a rough equivalent to your return mailing address. Your ISP gets this packet, sees the destination written on the outside, then sends it out to the internet. Once the data is retrieved the ISP looks at the IP address and returns the information to your device, all in fractions of a second.
The downside to this process is that anyone can read what’s on your postcard, as there’s nothing there to hide the information written on the outside. This is where encryption comes into play. With the right software enabled each packet of data you send will get wrapped in an envelope of cryptographic code before leaving your device. The postcard gets an envelope, but not just any envelope, one that’s impossible for anyone to open without the right key code. Each encryption method handles the specifics differently, but the end result is the same: your secret postcard is sent along without anyone except the intended recipient knowing what’s inside.
Encryption Creates Privacy
Encryption is great for everyday use and should be called upon whenever possible. Where net neutrality is concerned, though, it’s practically a prerequisite. Some of the biggest concerns with the loss of net neutrality is ISPs being able to throttle your connection or even block websites based on which subscription packages you purchase. They do this by examining the packets of data sent from your device. Did you request something from Facebook? Well, you didn’t pay for the social media premium plan, so you can’t access that.
What if the ISP can’t read your packets, though? What happens then? In all likelihood they simply pass the data on to its destination. If your Facebook request is encrypted, your ISP doesn’t know what you’re attempting to access and can’t prevent you from reaching it. There are ways for ISPs to work around this, of course, but then again, there are also workarounds for those workarounds. The point is encryption provides an excellent foundation for private access to the internet, even in the complete absence of net neutrality.
Method 1 – SSH Tunneling
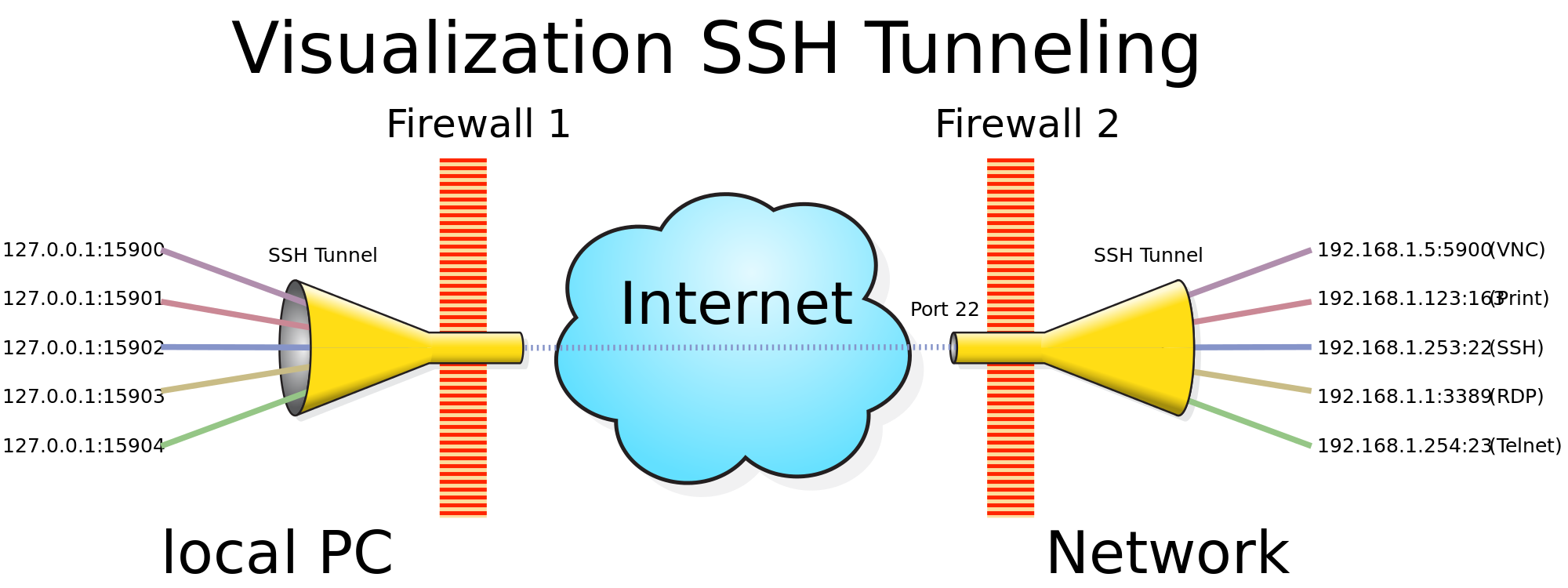
SSH tunneling, or secure shell tunneling, is an extremely common method of encryption that’s been around since the mid-90s. It’s estimated about 2 million people use it on a daily basis, a number that rises drastically if you include automated scripts and similar file transfers. SSH tunneling is generally used to send small files to a web host via terminal commands. It can be repurposed to do more than that, though, which is why it’s a viable method for helping to save net neutrality.
Benefits of SSH Tunnels
The biggest benefit of SSH tunneling is that most ISPs would never block these types of transfers. SSH is used for a lot of legitimate online work, especially by businesses. Blocking it would shut down a reliable and secure form of communication. We can take advantage of this fact by using SSH tunnels for more than just server-client transfers. By sending data with SSH encryption, you can slide right by anti-neutrality blockades and censorship firewalls to access a free and open web.
RELATED READING: How to Hide OpenVPN Traffic with an SSH Tunnel
Drawbacks to SSH Tunneling
SSH is an old protocol built when the internet was much smaller than it is today. Transfer speeds isn’t its strong point, which means downloading gigabyte movies or streaming HD videos doesn’t really work. This cuts out a vast swath of online content and prevents SSH tunneling from becoming a true competitor to things like VPNs.
How to Create an SSH Tunnel
If you know what you’re doing, creating an SSH tunnel is pretty easy. There are a few setup steps you’ll need to follow, though, along with some prerequisites you have to start with. We’ve written a complete guide to SSH tunneling, so go check it out and enjoy your new encrypted connection.
Method 2 – Shadowsocks (SOCKS5 Proxy)
The Socket Secure protocol is a method of exchanging packets between a server and client through the use of a proxy server. When using the newest SOCKS5 version of the protocol, data is also encrypted and authenticated, ensuring only the intended parties can access the proxy server. SOCKS is a deep level protocol that’s been in use since the early ’90s. In modern computing it’s mostly used as a circumvention tool to bypass internet filtering, especially in areas like China where censorship is a major concern.
Benefits of Using SOCKS5
The SOCKS protocol pretty much only exists as a tool for hacking and restoring internet freedom. It’s fast for an encryption method, offers a wide range of configuration options, and works on most devices, including smartphones and tablets. It’s also one of the few alternative encryption methods suitable for torrenting, as the way the protocol passes traffic through ports doesn’t interfere with swarm downloading.
Drawbacks of SOCKS5
The only real drawback to using SOCKS5 comes from the method of employment. If your VPN supports it natively, you can switch it on and not notice anything different, only better privacy and less online censorship. If you use shadowsocks it’s practically the same situation. Shadowsocks does require a dedicated server to work, however, which is complicated to set up on your own.
Using SOCKS5
Unless you have a VPN that supports SOCKS5, most people will turn to shadowsocks when it comes time to use an encrypted proxy. This piece of software was specifically designed to put the old protocol to use as a tool to restore online freedoms and defeat censorship. The tagline “If you want to keep a secret, you must also hide it from yourself” hints at just how effective shadowsocks can be. Your data will be so secure, you won’t even be able to hack yourself.
You’ll need two things to use shadowsocks: a server and a client. Server software is deployed remotely and serves as the actual proxy that passes data. Client software runs on your active device and handles the encryption and traffic routing. All of the instructions you need are on the shadowsocks website. Follow the steps below and you’ll have an incredible method of online privacy ready in minutes.
- Visit the shadowsocks website.
- Go to Download > Servers and follow the instructions to install on a remote host.
- Back on the shadowsocks site, go to Download > Clients to get the appropriate software for your device.
- Enter your server details into the client software.
- Connect to shadowsocks and browse the web with full privacy.
Method 3 – SSL/TLS Tunnel
Have you ever seen that little green padlock icon in your browser window, the one that shows up when you visit a webmail or online shopping site? That’s SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption at work. SSL is the predecessor to Transport Layer Security (TLS), both of which are encryption methods used to secure data on the web. The technology can easily be repurposed to do more than lock down a single connection to a single site. By creating an SSL tunnel you can encrypt all of your online traffic to break through censorship walls and bypass anti-neutrality filters with ease.
Benefits of SSL/TLS Tunnels
There are two huge benefits of using TLS tunnels to connect to the internet: the widespread nature of the protocol, and the low odds an ISP will block the traffic. As stated above, SSL/TLS is used by a large portion of the web today to send and receive ordinary traffic. When you buy something online, chances are the site is secured with SSL. This means ISPs are highly, highly unlikely to block this type of traffic, as doing so would shut down millions of legitimate connections. If you use an SSL tunnel to break through censorship barriers, chances are you’ll get through without any problems.
Drawbacks of SSL Tunnels
Speed is always an issue when using an alternative encryption method, as nothing really matches the balance provided by a good OpenVPN connection. SSL tunnels can suffer a bit from the same slowdown effect, especially if you’re downloading large files or streaming HD videos. SSL tunnels are also not supported by most VPNs, which means you’ll need to set up and configure your own using a separate piece of software, a method that can be complicated and time consuming.
How to Use SSL Tunnels
To use an SSL tunnel you’ll need to download the stunnel software, which, honestly, is best left to experienced hands. The site has tutorials and how-to guides for the entire process, but you’ll need extreme familiarity with terminal commands to get things running the right way.
Method 4 – Tor and Onion Networks

The Tor networks runs using onion routing, a process of wrapping data in multiple layers of encryption and passing it through an anonymizing network to remove traces of the host’s identity. Tor is best put to use with the Tor Browser, which runs in place of your current Firefox, Chrome, or Safari installation. With Tor you can often break through censorship efforts and access the free internet with ease. Best of all, you barely have to do anything out of the ordinary to utilize this method, just grab a browser and start surfing.
Benefits of Tor
Tor’s simplicity is probably its number one feature. The protocol can be used by a wide variety of software, especially the Tor Browser. All you have to do is download the file and run Tor, then you’re set. It’s also an incredible anonymizer, making it a great choice for people in restrictive areas where accessing the open ‘net could be dangerous to their livelihood.
Drawbacks of Tor
Speed is a huge issue with Tor. Utilizing the network means no videos, no torrents, and no streaming of any kind. By default a lot of modern web technologies are disabled in the browser, including any kind of applets or Java. Tor is best used for simple website browsing and e-mail communications. Using the browser itself also means your cloud storage or other outside connections won’t be encrypted or anonymized. The Tor network is also frequently blocked in the most restrictive of countries, making it useless in places like China or Syria.
How to Use Tor
This is the easy part. To use Tor, simply download the browser and run it like you would any browser software. It’s open source and works on a variety of platforms, including Android and iOS. You’ll notice an immediate drop in speed, but you can surf safe knowing your identity and location are safe. For more information about using the browser, check out our feature How to Use Tor: A Guide to Getting Started.
Method 5 – Obfsproxy
Obfsproxy, short for “obfuscation proxy”, is a tool that circumvents censorship by transforming encrypted traffic to make it unrecognizable to ISPs or other third parties. This is incredibly useful in scenarios where outgoing packets are scanned for signs of Tor encryption or VPN use and blocked as a result. Obfsproxy makes it nearly impossible to tell Tor/VPN packets from other packets, giving users another tool for bypassing censorship firewalls and gaining access to the open internet.
Benefits of Obfsproxy
Obfsproxy is best used in areas where net neutrality is long gone and ISPs are blocking things like Tor and VPNs. These extreme case scenarios are already in play in places like China, Ethiopia, Iran, and Syria, and they could spread as net neutrality dies a slow death. It doesn’t really slow down your traffic, but it can affect things like torrents or HD movie streams by nature of how those transfers are handled.
Drawbacks of Obfsproxy
Obfsproxy is slow and difficult to set up on your own. If your current VPN doesn’t support it by default, you’ll need to build your own VPN server and configure everything yourself. That can take time, it requires several pieces of external software, and it’s also not free.
How to Use Obfsproxy
If you need to use obfsproxy, your best bet is to sign up with a VPN service that offers it by default. Some of the more popular options include Mullvad and IVPN. NordVPN also offers the setting by default, along with a lot of other privacy and security options you’ll find useful. With one of these installed, you’ll simply run the software and select obfsproxy from the configuration menu.
Method 6 – VPN Encryption
Virtual private networks (VPNs) are incredible tools for saving net neutrality. They’re fast, easy to use, and they’re surprisingly effective, as well. Most VPNs use the OpenVPN protocol for encryption. This method is seen as a “nearly perfect” form of encryption that keeps data secure without being a heavy drain on resources. VPNs can use this and other protocols to mask your identity and provide a safe, open connection to the internet. Choose the right one and you’ll be set, no matter how strict the regulations are in your area!
Best VPNs for Saving Net Neutrality
The alternative encryption methods above do wonders for restoring free and open internet access. They’re best used by experienced hands, however, which can be a strong barrier to entry. VPNs by comparison are fast, easy to use, and even easier to install. Some of them even go the extra mile to provide access to some of the encryption protocols above, making them better choices for staying safe online. Below are three recommended VPNs that help make sure your online activities are as private as possible.
1. NordVPN

NordVPN is a great VPN provider no matter how you look at it. The service runs a huge network of over 5,100 servers in 60 different countries, offering fast connections to six continents and cities around the world. Some of these servers are also tasked to unique jobs, as well, including DDoS protection, double encryption, and the truly rare onion over VPN feature. Alongside these extras, all NordVPN users get to take advantage of a zero-logging policy that covers everything from traffic to bandwidth, IP addresses, and time stamps, DNS leak protection, an automatic kill switch, and 256-bit AES encryption on all connections on every device.
In addition to its double VPN and onion over VPN features mentioned above, NordVPN also offers both obfsproxy and SSL tunnels through its apps. All you have to do is dive into the configuration settings and switch them on, then you’re surfing the web with a free, open, and private connection.
Read our full NordVPN review.
- Highly affordable plans
- Over 5,400 servers in 61 countries
- Torrenting is explicitly permitted
- Based in Panama
- 24/7 Live Chat.
- Some servers can be slow and unreliable
- Refund processing can take up to 30 days.
2. Surfshark

The newest VPN on our list by a stretch, but one built for a post-Net Neutrality world. Launched in 2019, Surfshark has a litany of advanced provisions that will enable you to dodge censorship, hide from your ISP, and unblock websites and apps anywhere in the world.
At the core of Surfshark’s offering is NSA-grade 256-AES-GCM encryption, with tunneling options including OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPSec, WireGuard, and even Shadowsocks on Windows and Android devices. You can configure individual Wi-Fi networks with different protocols, enabling you to customize your security based on where you are.
Additionally, Surfshark’s Camouflage obfuscation kicks in whenever it detects websites or ISPs trying to sniff out your VPN traffic. This makes your encrypted traffic all but unblockable–an important consideration given the direction things are heading. And of course, Surfshark keeps no logs–their RAM-only network guarantees this beyond the legal bindings of their privacy policy.
- Break through harsh censorship to securely access social media and foreign news sites
- Unlimited server switching
- Bitcoin, Etherium, and other cryptocurrencies accepted as payment
- Logging policy independently audited and verified
- Support staff manned by actual human beings 24/7.
- Connection speeds won't impress users of other high-end VPNs
- Power users may wish for more settings to fiddle with.
Read our full Surfshark review.
3. ExpressVPN

ExpressVPN is one of the fastest VPNs around. They accomplish this through a network of over 3,000 servers distributed in 94 countries around the world, each one finely tuned for low latency and speedy video streams by default. Connections are always secured with 256-bit AES to lock your data down tight, and you’ll also be protected by a zero-logging policy on traffic, DNS leak protection, and an automatic kill switch. Best of all, ExpressVPN is incredibly easy to use. Simply sign up, run the software, then connect to the fastest server with a single click.
ExpressVPN allows for SSL tunnels on its main apps, which provides similar obfuscation as the other methods listed above. It’s a great extra that helps defeat censorship blocks and restore an open internet connection no matter where you live.
Read our full ExpressVPN review.
- Unblocking Netflix USA, iPlayer, Amazon Prime
- Super fast, reliable connection
- Secure encryption & VPN protocols
- No personal information logs kept
- Live chat support available.
- High cost for month-to-month users.
Conclusion
Saving net neutrality for the world is a long and involved process that requires constant fighting with local governments and powerful corporations. While this battle rages on, running a VPN or using alternative encryption methods can ensure your connection is safe and anonymous for full access to the open web. Know of any other services that help restore net neutrality? Let us know in the comments below!
If you need a VPN for a short while when traveling for example, you can get our top ranked VPN free of charge. NordVPN includes a 30-day money-back guarantee. You will need to pay for the subscription, that’s a fact, but it allows full access for 30 days and then you cancel for a full refund. Their no-questions-asked cancellation policy lives up to its name.

You offered benefits and drawbacks of every method except for VPN, but as with everything else, there are drawbacks to using a VPN. For one, not all VPNs are created equal, as you imply by promoting “the best VPNs for saving Net neutrality.” I can’t even begin to name all the potential problems, like logging your activity and selling it to third parties or worse, giving it to governments. Many of them are not fast at all. And one of the biggest problems I’ve experienced is being blocked by websites because my traffic goes through a VPN, a topic your website covers in a different article.
“With net neutrality officially repealed in the United States, the future of a free and open internet hangs on the balance.”
Really?
So you are saying that before mid 2015, there was no free and open Internet?
By the way, do you it’s Internet, with a capital I?
Why don’t you find better way to promote the VPNs you are pimping rather than fear mongering based on a propaganda?
In other words, do you understand few of the facts about the Internet, among them, the US does not control the Internet, it is a global network, “Net Neutrality” never guaranteed “free and open internet”, neither guaranteed privacy or enforced encryption. Try reading the full text of the rules, otherwise it makes you lack credibility.