SNMP Traps Explained – Best Tools to Receive and Handle Traps
Although most network administrators are familiar with SNMP or at least have heard about it, not too many have experience with SNMP traps. Using SNMP polling has been the primary way of monitoring network-attached equipment for as long as monitoring tools have existed. SNMP traps, on the other hand, have not enjoyed the same relative popularity, especially in recent years. In fact, although many devices have the ability to generate traps built right into their operating system or firmware. Not many people actually use the feature. For those who do—or for those planning to start doing it—finding tools can be a challenging endeavour. There are not that many tools available and a typical search will return more SNMP monitoring tools than traps tools, no matter what search terms you use. We’ve done some of the tedious work for you and we’re glad to bring this list of some of the best SNMP trap tools.
We’ll start off our discussion today by having a look at SNMP. Although our goal is not to make you an SNMP expert, the different features of the available tools will be easier to understand once you know more about the protocol. We’ll then specifically discuss SNMP traps. We’ll tell you what they are, how they work, and what they can do for you. Finally, we’ll hit the core of the matter and review some of the best SNMP trap tools we could find.
SNMP In A Nutshell
Despite its somewhat misleading name SNMP–which stands for Simple Network Management Protocol–is relatively complex technology that can be used to remotely monitor, configure and control many different types of networking equipment. It is also an alerting system which allows SNMP-enabled devices to send out notifications in response to certain events.
Fortunately, as complex as this simple technology may be, you don’t have to know everything about SNMP to use it. SNMP-based management tools, no matter what type of tool they are, typically hide most of the details from you. For now, suffice to say that SNMP is mostly used by monitoring tools to read device’s operational parameters. SNMP is also used for remote management and configuration of SNMP-enabled devices although this use of the protocol is much less common than it once was, mainly because better technologies have been developed.
As for SNMP Traps, they are short messages that are sent by SNMP-enabled devices to trap receiver in response to predefined events. More about that later.
SNMP Explained
Most texts about SNMP will tell you about MIBs and OIDs. After all, they are the basic building-blocks of SNMP. We’ll try to keep our discussion less technical. Our goal is not to make you an SNMP expert but rather to give you enough information so that you can understand the basics of SNMP in order to better appreciate our tool reviews.
Let’s first talk about the security of SNMP… or lack thereof. SNMP requests and responses are not encrypted and can therefore easily be intercepted. There’s also not much authentication built into SNMP. Enabled devices are configured with something called “Community Strings” which can be either read-only or read-write. Whenever an SNMP manager sends a request to an enabled device, it included a community string which must match what’s configured on the equipment. This is pretty much all the security there is.
In the context of network monitoring or remote configuration, an SNMP manager—which is often a monitoring tool—gets or sets a specific parameter corresponding to what it is trying to do. Let’s take a network monitoring tool as an example. Of particular interest when it comes to network monitoring are a few parameters called interface counters. There’s a pair of them for each network interface of an SNMP-enabled device counting the bytes in and the bytes out of the interface. By reading these values periodically at know intervals, the monitoring tool can compute the average number of bits per second that were transported during the polling interval.
SNMP Traps — The Other Feature Of SNMP
SNMP traps are an often-forgotten feature of the SNMP protocol. They once were much more commonly used but it seems that it is not so much the case anymore. It is kind of a shame as it is a great feature. In a nutshell, SNMP traps are alert messages that are sent by SNMP-enabled devices to “trap receivers”. As for the receivers, they are software tools running on a computer that receives the traps and perform various actions such as logging them, displaying on-screen alerts, sending out email or SMS alert messages, etc. In a way, SNMP traps are not unlike syslog messages.
Many SNMP-enabled devices can be configured so that certain events will generate traps. For instance, a router could send a trap whenever an interface goes down, a probable indication that something is wrong. How traps are configured on each device varies between vendors and is beyond the scope of this post but it’s typically relatively easy. Often, devices are set up to send traps in reaction to any event, letting the receiver software sort them out and figure out which ones should be addressed.
Another important parameter to configure on SNMP enabled devices is the traps destination. Many devices will send them by default to any device which has sent an SNMP request. Often, these will be monitoring tools that can’t handle traps and will simply ignore them. For that reason, it is always preferable to configure SNMP-enabled devices with a destination to send traps to. It will ensure that none of the traps are ignored.
The Best SNMP Trap Tools
There are not that many tools out there that are made to receive SNMP traps. Most of the tools we’ve found are actually SNMP network monitoring tools that include the ability to receive and handle traps. Sometimes, it comes as an add-on module while it sometimes is built right into the software. We’ve also included a couple of dedicated SNMP trap receivers that you might want to try, especially if you already have a monitoring solution in place and it can’t handle traps.
1. SolarWinds SNMP Trap Receiver
SolarWinds is certainly one of the best-known makers of network and system administration tools. Through its twenty years of existence, the company has brought us some of the best tools ever. Its flagship product, the Network Performance Monitor, is recognized by many as one of the very best SNMP network bandwidth monitoring tool. Even better, SolarWinds also makes some excellent free tools, each addressing a specific need of network and system administrators. Among those are tools like the Kiwi Syslog Server and the Advanced Subnet Calculator, just to name a few.
The SolarWinds SNMP Trap Receiver is a tool that is part of the SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset, a bundle of some 60 tools useful to network administrators and engineers. We’ll get back to the toolset in a moment.
The software constantly listens for SNMP traps generated by SNMP-enabled devices. When it receives one, its details are logged along with the time, IP address, hostname, and trap type. This information can be used for analysis and correlation. This tool doesn’t provide much in terms of alerting capabilities. Its primary use is in verifying that a trap source is configured and functioning properly. For that purpose, it is one of the best tools available.
As part of the SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset, the SNMP Trap receiver sells for $1495. While this might seem like a hefty price, you must take into consideration that there are some 60 different tools included in that bundle. And if you want to give the tool a try, a free 14-day trial is available from SolarWinds.
2. SolarWinds SNMP Trap Editor
Another useful tool which is also part of the SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset is the SNMP Trap Editor. This is a tool you can use when testing your SNMP trap receiver configuration. Simply put, the tool enables you to modify SNMP trap templates and mimic critical alerts to ensure management systems are functioning properly. It is a highly specialized tool unlike any other we’ve seen. The best way to fully appreciate what this tool can do for you is to take advantage of the available 14-day trial of the Engineer’s Toolset and give it a test run.
More About The SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset
The SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset includes several dedicated troubleshooting tools. Some of the included tools—such as the subnet calculator, for example—are available for free from SolarWinds but most are exclusive to this toolset and cannot be otherwise acquired. There are tools like Ping Sweep, DNS Analyzer and TraceRoute can be used to perform network diagnostics and help resolve complex network issues quickly. For the security-oriented administrators, some of the toolset’s tools can be used to simulate attacks and help identify vulnerabilities.
The SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset also boasts excellent monitoring and alerting capabilities. Some of its tools can monitor your devices and raise alerts for availability or health issues. You can also use some of the included tools for configuration management and log consolidation.
Here are some of the other tools you’ll find in the SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset:
- Port Scanner
- Switch Port Mapper
- SNMP sweep
- IP Network Browser
- MAC Address Discovery
- Ping Sweep
- Response Time Monitor
- CPU Monitor
- Memory Monitor
- Interface Monitor
- TraceRoute
- Router Password Decryption
- SNMP Brute Force Attack
- SNMP Dictionary Attack
- Config Compare, Downloader, Uploader, and Editor
- Subnet Calculator
- DHCP Scope Monitor
- DNS Structure Analyzer
- DNS Audit
- IP Address Management
With that many tools included in the SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset, there is no way we can describe them all here. Your best bet is to give it a try and see for yourself what it can do for you. And with a free 14-day trial available, there is really no reason not to try it.
3. SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
The SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, or NPM, is a complete integrated network monitoring solution packed with features. The product is easy to use and easy to install. It is also highly flexible and its dashboard, views, and charts can be customized at will. Setup requires little effort and you can start monitoring within minutes. NPM is also highly scalable and it can be used to monitor networks of almost any size from the smallest ones to huge corporate networks spanning multiple sites.
The SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor periodically polls your networking equipment to read their interface counters, computes the bandwidth utilization, and displays it as graphs showing its evolution over time. An auto-discovery engine makes initial setup super easy. Adding devices to it is just as easy and only requires that you specify a device’s IP address and pick which parameter you want to monitor.
The SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor also has many advanced features. It can, for instance, built network maps. It can also display the critical path between two devices, a handy feature when troubleshooting slowdowns. And of course, it can also receive SNMP traps and generate intelligent network alerts when device events occur. The tool’s SNMP trap receiver lets you easily create intelligent alerts based on simple or complex nested trigger conditions, defined parent/child dependencies, and network topology.
Prices for the SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor start at $2 995 for up to 100 monitored elements and varies according to the number of monitored elements. If you’d rather try the product before buying it, a free and device-unlimited 30-day trial version can be downloaded from SolarWinds.
4. ManageEngine OpUtils
ManageEngine is another well-known name in the field of network and system administration tools. ManageEngine OpUtils is a toolset that is available in both a free and a Professional edition. It includes over 25 (11 in the free version) different tools, each performing a specific function.
When it comes to SNMP tools, ManageEngine OpUtils includes a few. There’s a MIB Viewer to retrieve and analyze information about a MIB or a specific MIB OID/node from a MIB file. SNMP Graph is another included utility which gathers real-time data and draws a graph for any SNMP IP node. There’s also the Community Checker, a tool that fetches the read and write community strings of SNMP-enabled devices on your network. Finally, there’s the Trap Receiver which receives and displays SNMP traps. It can be configured to send email notifications on receipt of a trap.
Prices for the Professional edition of ManageEngine OpUtils start at $345 and a free 30-day trial version is available.
5. Paessler Router Traffic Grapher (PRTG)
The Paessler Router Traffic Grapher, or PRTG, is another bandwidth monitoring tool with SNMP trap capabilities. PRTG is a feature-rich product. The software come with a selection of user interfaces. You may choose between a native Windows enterprise console, an Ajax-based web interface as well as mobile apps for Android and iOS. PRTG can monitor devices using SNMP, WMI, NetFlow, and Sflow. It also has tons of reports that can be viewed as HTML or PDF or exported to CSV or XML to be processed externally.
The monitoring possibilities of PRTG are almost endless and sensors—you can think of them as extensions of the product—are available for all sorts of purposes. There is, for instance, a Trap Receiver Sensor which collects incoming trap messages. PRTG uses it to receive data and, depending on the filter rule, trigger an alarm. The sensor displays the total number of traps received per second, as well as the number of messages that are classified as warnings or errors. It also indicates how many trap packets are lost per second. When using this sensor, you can set your own filter rules. The Trap Receiver Sensor lets you analyze traps and filter them according to date, source, agents, bindings, and more.
PRTG is available in a free version that will limit your monitoring to no more than 100 sensors. Each parameter you want to monitor counts as one sensor. For example, monitoring bandwidth on each port of a 48-port switch will require 48 sensors. Each instance of the SNMP Trap receiver sensor also counts as one. For more than 100 sensors you’ll need a paid license which starts at $1600 for up to 500 sensors, including the first year of maintenance. A free 30-day trial version is also available.
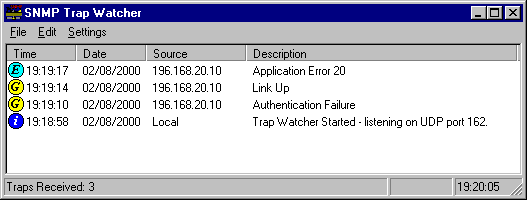
6. SNMP Trap Watcher
Last on our list is a freeware tool from BTT software called SNMP Trap Watcher. This tool can be used to receive SNMP Traps from network equipment, including routers, switches, and workstations. It is a pretty basic tool whose only function is to receive traps and display in on its graphical dashboard. It can also be configured to send traps by email
SNMP Trap Watcher also allows SNMP traps to be filtered by string or by type (Enterprise specific or Generic). Using the Decode Window, and selecting a specific trap from the list will display a full decode of the trap, a useful option when debugging network equipment configurations.
SNMP Trap Watcher is provided as freeware. It will run on any version of Windows and does not require to be installed, making it a great portable tool. All you need to do to use SNMP Trap Watcher is to download it, unzip it and run it.