The Complete Guide To Protecting Your Privacy Online
It is a well known fact that invasion of online privacy has become the rule rather than the exception. The source of the threat is not just phishing websites and malicious tracking sources but some of the most trusted websites and web services. Search engines, for instance, use many parameters to identify the location of visitors under the guise of providing users with “better and more personalized search results”. Likewise, users have become so blind to sharing their personal data online that tracking anyone can simply mean looking up their name on Google or checking out their Facebook profile.
For instance, a WhoisLookup can provide the complete details of a website owner including his/her address, phone number, etc (provided Domain Privacy is not enabled). Even social media websites such as Facebook provide periodic prompts for tagging, sharing, and providing personal information which makes one more vulnerable to online and real life scammers. Which brings me to the question: why does Gmail prompt me to provide a mobile number for “account recovery”? Such options should not be presented repeatedly when one logs into an online account. And if that’s not enough, we recently discovered that a security vulnerability on Facebook gave advertisers and other third parties a way to access user accounts and personal information (as explained by Symantec Corp). This frustratingly complacent act by Facebook comes as no surprise, considering their history of blunders. For instance, they earlier had the audacity to change their user information policy, granting themselves permanent rights to users’ photos, wall posts and other information even after a user closes his/her account. This policy was later reverted after heavy criticism from all over the globe.

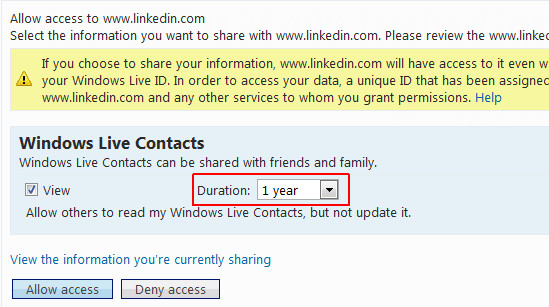
It is also worth mentioning here that you might also want to check out how your contact list is saved by web services. For example, when you check contacts to be invited to LinkedIn via Windows Live Mail, there is a drop down box which provides the amount of time LinkedIn can access your contact list. The least amount of time is 1 day but that’s not the option selected by default. The option selected by default is 1 year. As if one day of access to the contact list wasn’t enough. The point is that you can no longer trust any web service, search engine, online extension and the likes when it comes to online privacy. One can easily avoid data theft, invasion of personal privacy and security by taking some small but important measures. In this post, we will provide you with a complete guide as to how you can protect your online privacy. As far as I am concerned, users should not be forced or tricked into providing personal information which they don’t want to share. No service provider should have the right to show forceful prompts asking for personal data. Another threat to privacy comes from extensions which gather your personal information and even work in Incognito mode, which makes them acquire access to the most private data.
Anonymous Browsing, Proxies and VPN
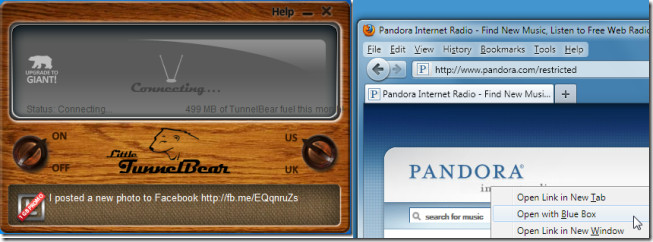
Using an anonymous proxy or VPN to browse through the Internet is much safer as harmful websites can attempt to log IP addresses for malicious purposes. Certain spyware applications and harmful codes also require personal IP addresses in order to initiate an attack. Similarly, hackers try to use IP information in order to obtain home addresses, credit card information, social security numbers and bank account credentials. Using an anonymous proxy tricks such malicious sources by providing them with a fake IP, which protects your computer’s security from being compromised. Going through a third-party network by using a VPN also shelters one from such online tracking agents that attempt to profile user activities. Anonymous browsing can help you avoid being tracked by websites, malware, advertisers, etc which use numerous parameters to determine your age, location, buying preferences, habits, etc. to tempt you. You can use some of our recommended VPN and Proxy based applications and extensions such as Blue Box Proxy, Go 2 Proxy (Firefox Extensions), Proxy Py Web Proxy (Chrome Extension), TrustConnect, TunnelBear, CyberGhost and Free VPN (Applications).
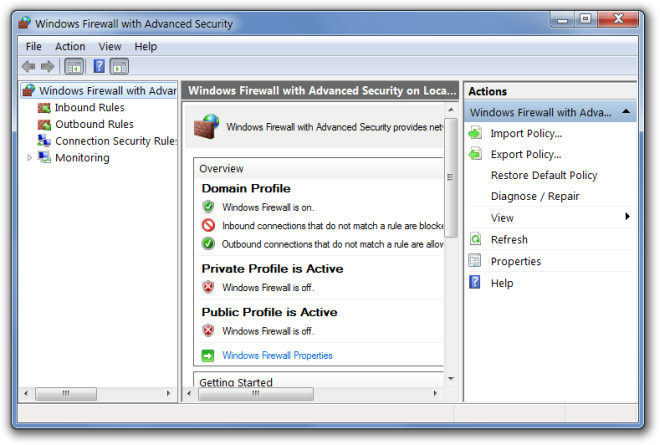
Use A Firewall
A firewall is meant to permit or deny network transmissions based upon a set of rules and is used for network protection to prevent unauthorized access. While it permits legitimate communication to pass, it blocks suspicious or unauthorized sources from accessing your network and hence your personal information. Normally, offices use hardware firewalls such as Pixs or/and a software firewall such as ISA (Internet Service Acceleration Server). Home users can easily benefit from the built-in Windows firewall or get one from a repository of their operating system provider (e.g. Ubuntu users can use the Ubuntu Software Center to find and install a firewall). You can also use an anti-virus which comes with a built-in Firewall such as AVG or Avast. Having a firewall makes it difficult for user profiling agents to track you down as unauthorized transmissions are denied access by your Firewall. For example, if you turn on your Windows Firewall, you will realize that some websites which provide generic ads based on your location will have problem figuring out your city name and provide incorrect ads. For example, if you live in London and visit a website which shows you London based ads or ads with the word “London” in them (based on your detected location), then turning on the Firewall will lead to inaccurate advertisement. For example, the ad may have your city labeled as “Oxford” as that may be the area from where your ISP may be originating. The point is that the user profiling agent will not be able to get past the detection of the location of your ISP as it would not be able to access your personal information for profiling your browsing data. Depending upon your Firewall type and settings, you can strictly restrict incoming and outgoing data transmissions and access to your personal information.
Restriction Of Browser Extension Access And Incognito Mode
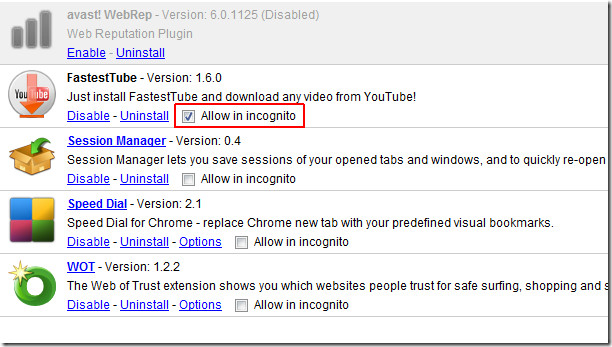
When you go into the Incognito mode of a browser, the pages you view do not appear in your browser history, search history, and do not leave traces, like cookies, on your computer (after you close the browser window). While going into incognito mode does not normally affect behavior of user profiling agents, yet it can be helpful to get rid of tracking cookies (which can be used for tracking user’s browsing habits by a third-party source) and other such temporary files. It must be noted that you should avoid allowing extensions to have access to user data in Incognito mode as this will result in the elimination of the utility of this mode. By default, extensions are not enabled in Incognito mode but you can make sure of that by going to the add-ons manager of your browser. In Chrome this can be done from Tools –> Extensions (make sure “Allow in incognito” option is unchecked). For Firefox, you can go to Tools -> Add-ons -> options (for the specific extension). Similarly, Opera users can manage Incognito options from Menu -> Extensions -> Manage Extensions -> Privacy.
Note: Disabling extensions from Incognito mode is not possible until you switch back to the normal mode.
Use A Link Scanner
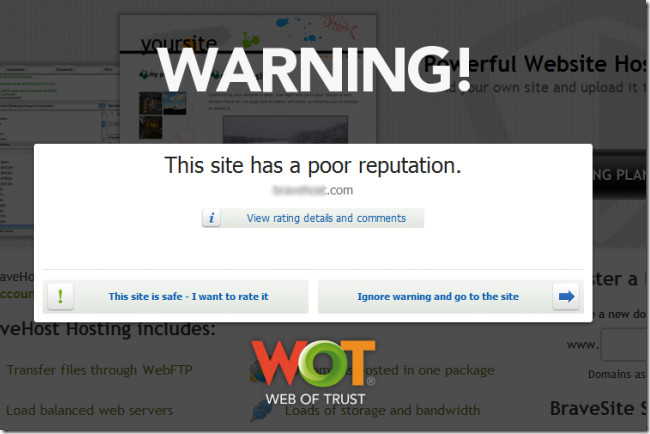
Certain anti viruses such as Avast and browser extensions like WOT provide automatic link scanning. Hence, you can use a reliable extension such as WOT (Web Of trust) or an Anti-Virus with a link scanner to instantly identify the reputation of a website. Such link scanners provide ratings for websites that you visit and alert you in case you come across a harmful website. Reliable link scanners like WOT are available for many commonly used browsers such as Chrome and Firefox. You can also use the following web services to scan any website for malware, Link Scanner and URL Void.
Adjust Your Social Network Settings
While many people like keeping their personal information public or freely sharing it across their social media network, this can lead to many issues including access of personal data by an unauthorized user. Online account hacking is not just performed by seasoned hackers but also common users who try to guess user information based on words expressed in the victims profile. Moreover, your public pictures can be easily saved to create clone profiles to impersonate you. For this reason, you should be very specific about the kind of information that you keep publicly accessible. For example, it may not be a good idea to keep personal and family pictures, house address, mobile phone information etc. to be publicly available. It can also be useful to hide your friends list for people who may not be added inside your social circle.
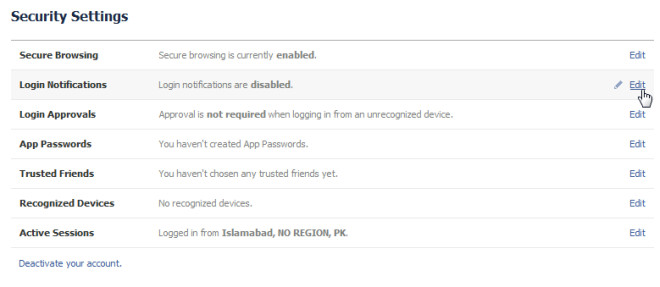
Use Secure Browsing Sessions
HTTPS Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) ensures secure communication between your computer and a web server. Using HTTPS can provide encryption and secure identification for your online sessions. For this reason, it might be a good idea to head over to your Security Settings on Facebook and other websites which offer secure HTTPS browsing. For example, you can enable the secure browsing feature, login notifications (to get notified when your Facebook account is accessed), Login approval for unrecognized devices, application passwords, etc. In Facebook, these settings can be accessed from clicking on the Arrow next to “Home” and selecting Account Settings. To make your browsing sessions safer, you can also check out the following extensions:
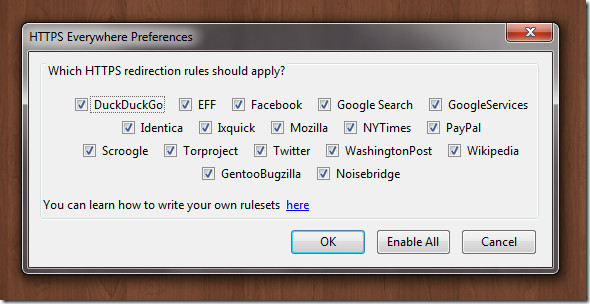
HTTPS Finder and HTTPS Everywhere (Firefox Extensions)
Facebook Secure Connection (Force HTTPS and SSL) (Extension for Chrome)
Keep A Complicated Password
Keeping a complicated password is one of the best ways to secure an account. Many malicious sources use dictionary word combinations to break into an account. Keeping a password with a combination of digits, capital letters and non-dictionary words makes it difficult for malicious agents to break it. An example of a complicated password would be @dd!ct!v3Tip$ instead of addictivetips. But make sure that the password is easy enough to remember. For this reason, it might be reasonably safe to use 1 digit and one non hexadecimal character. An example can be Addictivetip$ (with one capital word and a dollar sign).
Avoid Public Computers
Avoid using public computers like those in libraries and internet cafes for logging into your Facebook account as any traces of your password may be extractable (via keyloggers, for instance) by people who use these public computers. Moreover, there may be certain software installed on such systems that keep a track of passwords and other user data. Hence, public places perhaps have one of the most unsecure networks and computers.
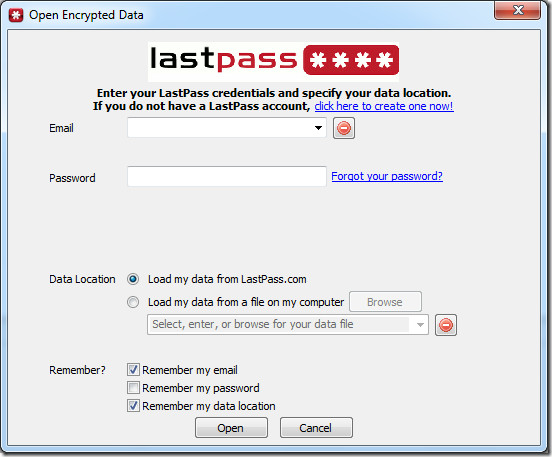
Don’t Save Passwords In Your Browser
Avoid saving passwords by using default options like the Firefox Save Password option. Such passwords are easily viewable by anyone who uses the system and can be extracted by spyware. However, you may use LastPass or a password management application such as Secure Password Storage. While extensions such as LastPass provide centralized password management of your online account passwords, applications such as Secure Password Storage can be handy to securely store your login credentials offline. This way, you can avoid the hassle of having to remember a large number of account credentials for multiple accounts and also save the account data in a secure manner.
Using the above mentioned precautions, applications and extensions, you can easily secure everything from your basic data to passwords for online accounts, browsing history, etc. from being compromised. Most privacy invasions do not merely occur due to lack of user knowledge but rather the negligence and excessive trust that users have for certain online services. Perhaps the best way to be secure is to revoke that trust and be more cautious regarding the usage of your information. It does not hurt to pause for a second and figure out the relevant checkboxes and drop down menus which you are provided by websites requesting your data. The common habit of accepting any kind of user license agreement and clicking on the Next button is definitely part of the problem. While it is impossible to read through the convoluted user agreements, you can still check out the amount of time your shared data will be kept by the service provider and who may have access to it. The LinkedIn example given earlier should be sufficient to elaborate this point. It must be noted that the applications, extensions and precautions mentioned in this article are mere suggestions which you can use to secure your private data and online privacy.

1. Noscript
2. TrackerBlock
3. Ccleaner
What abt TOR browser?.. its safe and free of cost..